Medical Library
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Tear
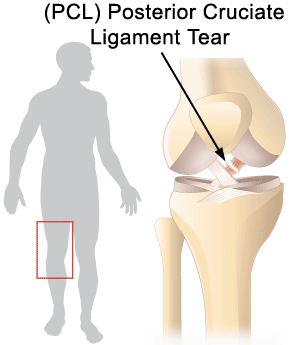
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is stronger and less commonly injured. Motor vehicle accident, when the knee(s) forcefully impact the car dashboard, is a common mechanism of injury. Initial treatment includes rest, ice, elevation, and compression. Physical therapy consisting of progressive strengthening and functional exercise may facilitate recovery. Surgery is not typically required.
Possible Treatments
- Aerobic/Endurance Exercise Video
- Core Strengthening Video
- Cryotherapy or Cold Therapy Video
- Electrotherapeutic Modalities
- Isometric Exercise Video
- Knee Active Range of Motion Video
- Knee Passive Range of Motion Video
- Knee Resistive Range of Motion Video
- Proprioception Exercises Video
- Physical Agents
- Soft Tissue Mobilization Video
- Stretching/Flexibility Exercise Video
- Aerobic/Endurance Exercise
Possible Treatment Goals
- Improve Balance
- Improve ability to bear weight/stand on the leg(s)
- Decrease Risk of Reoccurrence
- Improve Fitness
- Improve Function
- Improve Muscle Strength and Power
- Increase Oxygen to Tissues
- Improve Proprioception
- Improve Range of Motion
- Self-care of Symptoms
- Improve Tolerance for Prolonged Activities
- Improve Wound Healing
Additional Resources
Knee Articles- Quadriceps Muscle Strains
- Meniscal Tears
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Tear
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Tear
- Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Tears
- Anterior Knee Pain
- Patello-femoral Pain (Commonly Called Chondromalacia Patella)
- Patellar Tendinitis (Jumper's Knee)
- Knee Osteoarthritis
- Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome (ITBS)
- Knee Replacement
Pick a Body Area
Other Choices
Systemic Treatments Exercises For Physicians NewslettersDisclaimer
The information in this medical library is intended for informational and educational purposes only and in no way should be taken to be the provision or practice of physical therapy, medical, or professional healthcare advice or services. The information should not be considered complete or exhaustive and should not be used for diagnostic or treatment purposes without first consulting with your physical therapist, occupational therapist, physician or other healthcare provider. The owners of this website accept no responsibility for the misuse of information contained within this website.
